Maia de la Calle, Rutgers Economic Advisory Service (R/ECON™)
In the past few weeks, discussions on the “Great Resignation” and labor shortages have permeated news cycles. These phenomena, characterized by (1) record-high levels of voluntary resignations and (2) job openings surpassing the number of unemployed workers, are being described as major “threats” to the nation’s post-pandemic economic recovery efforts. New Jersey is one of eight states that has more unemployed workers than job openings—0.9 openings per worker. This finding is attributed, in part, to the state’s weak post-pandemic tourism performance. At the same time, New Jersey’s October 2021 unemployment rate of 7.0 percent is the third-highest in the nation,[1] far exceeding the national average (4.6 percent).[2]
For the past ten months, New Jersey’s employment numbers have been growing steadily. To better understand the pandemic’s impact on employment and economic recovery in New Jersey, Figure 1 illustrates the changes in the labor force by sector, relative to pre-pandemic levels (October 2019).
Figure 1. Labor force changes* by class of worker since prior to COVID-19 outbreak New Jersey
October 2019-October 2021
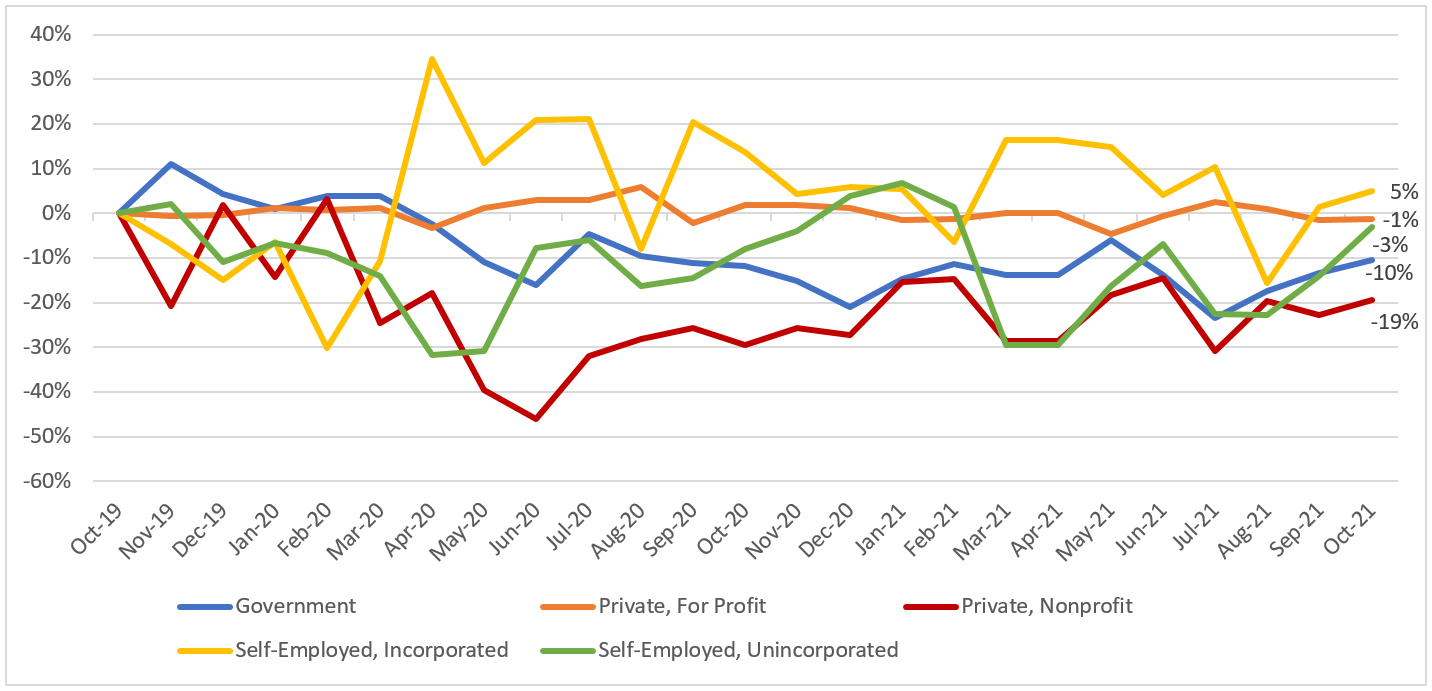
Source: Own calculations of the Current Population Survey non–seasonally adjusted state labor force estimates
Some sectors that have fully or nearly fully recovered their pre-pandemic workforce levels include the self-employed (incorporated) and private, for profit. The latter represented 73 percent of the state’s workforce before the pandemic (i.e., the largest sector), thus, its rebound translates to a significant contribution to the state’s overall job recovery. The growth of self-employed workers observed in New Jersey comports with national trends,[3] suggesting that people are favoring jobs that provide time flexibility and the possibility to work remotely, amongst other benefits.
For more information, download the full report.
References
[1] BLS (2021). Unemployment rate for states. Local area unemployment statistics. Retrieved from: https://www.bls.gov/web/laus/laumstrk.htm
[2] BLS (2021). Unemployment Rate. Labor force statistics from the Current Population Survey. Retrieved from: https://data.bls.gov/timeseries/LNS14000000
[3] Kochhar, R. (2021). “The self-employed are back at work in pre-covid 19 numbers but their businesses have smaller payrolls.” The Pew Charitable Trusts, November 3, 2021. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2021/11/03/the-self-employed-are-back-at-work-in-pre-covid-19-numbers-but-their-businesses-have-smaller-payrolls/
