In a new article, “Political Partisanship and Transportation Reform,” (Journal of the American Planning Association, Sept. 2021) Nicholas J. Klein of Cornell University, Bloustein School associate professor Kelcie Ralph, Calvin Thigpen, director of policy research at Lime, and Anne Brown of the University of Oregon, look at the nature of support for changing the automobile-oriented status quo by surveying 600 US adults.
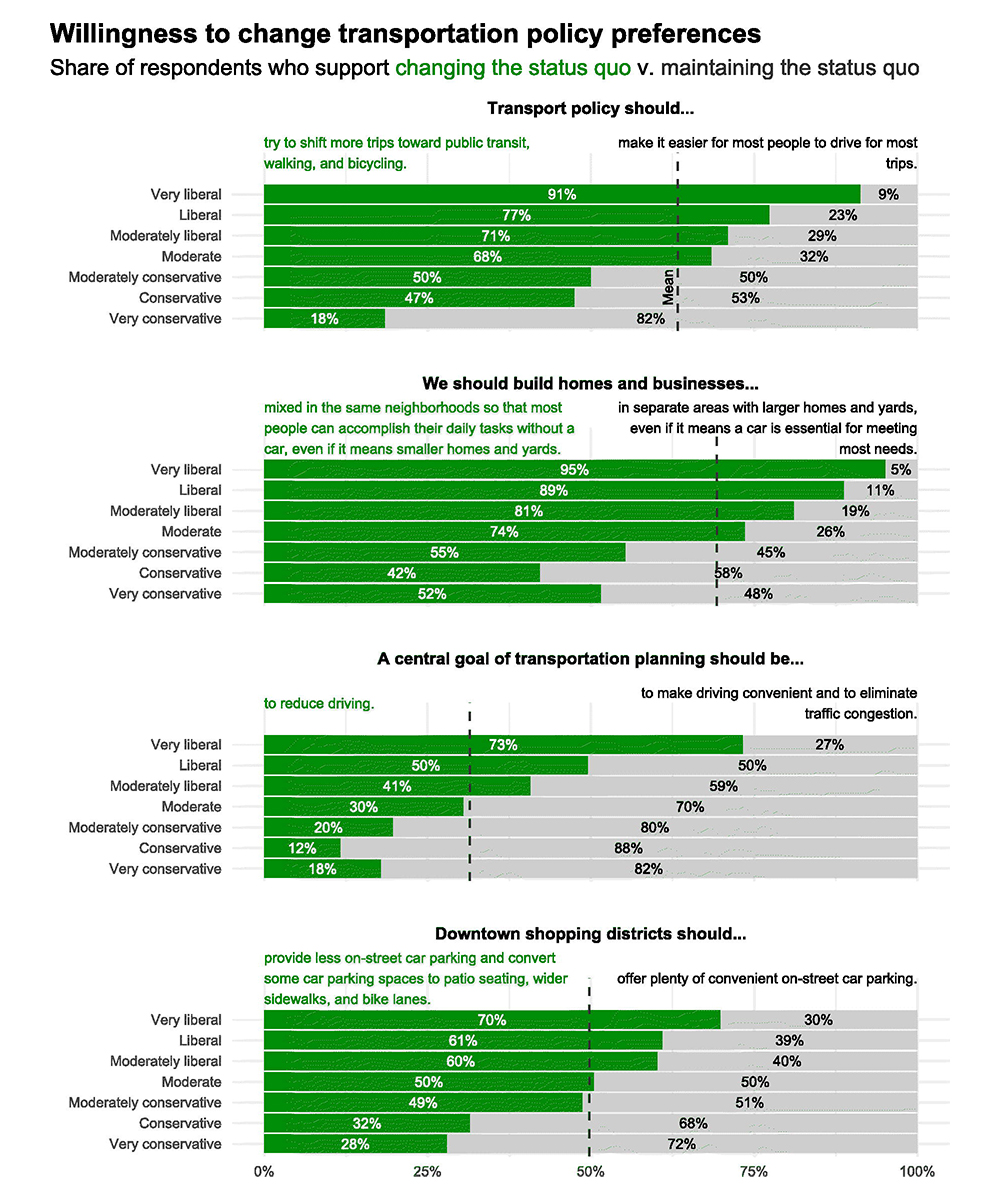
The authors find considerable support for some changes to the transportation system. For instance, a majority support shifting trips towards walking, biking, and transit or mixing homes and businesses in the same neighborhoods. The public, however, is evenly divided on repurposing downtown parking and opposed to reducing driving.
Above and beyond these broad trends, the authors uncovered important partisan divides. For example, liberals and moderates were likely than conservatives to support shifting some trips to walking, biking, and transit and mixing homes and businesses in the same neighborhood.
To better understand the increasingly partisan nature of transportation, the authors examined transportation-related values, beliefs about the possibility of change, self-interest, and transport. They find that partisan policy preferences dovetail closely with values and beliefs about change. In short, liberals and moderates were more likely to believe that changes to infrastructure and travel patterns are possible; in turn, those same respondents were much more likely to embrace changes to the status quo (by a 35 percentage point margin).
The results for the two remaining pathways—self-interest and knowledge—were mixed. Their research shows a strong link between travel behavior (a proxy for self-interest) and policy preferences — People who primarily traveled without a car and/or who did not own a car were more likely to embrace reform. However, these measures of self-interest did not vary by political ideology. Most Americans, regardless of their political leanings, use an automobile for most trips. The patterns for knowledge were nearly reversed. Four of the five measures of knowledge were partisan, with conservative respondents typically more likely to misunderstand foundational facts. However, just two of these facts were linked to policy preferences: the rate of U.S. car ownership and induced demand.
These four pathways explain most, but not all, of the partisanship in transportation policy preferences. Very Conservative respondents were less supportive of transportation reform efforts, even after accounting for their values, beliefs, self-interest, and knowledge.
For an in-depth look at partisanship and transportation policy and what they imply for planners, policymakers and advocates, the full article may be found at 10.1080/01944363.2021.1965495.
