Committed to the themes of health in all policies, healthy communities, and the culture of health, the Bloustein School intertwines these topics through the planning, policy, and health curricula. In September 2019, a group of faculty and staff developed a series of courses that would highlight the various themes and enable students to showcase the interconnected nature of the school’s disciplines.
Over the course of several months, faculty members guided a graduate planning studio, a graduate policy practicum, an undergraduate design class, and an independent study around these topics. Despite the challenges posed by COVID-19 in the spring, students completed significant deliverables for clients, which are featured here.
Future courses will also incorporate the themes into the school’s newest degree program, urban and public informatics.
By linking improved transit and environmental interactions with preventive and health care, this innovative design encourages a culture of health by providing fair and just opportunities for health and well-being for everyone.
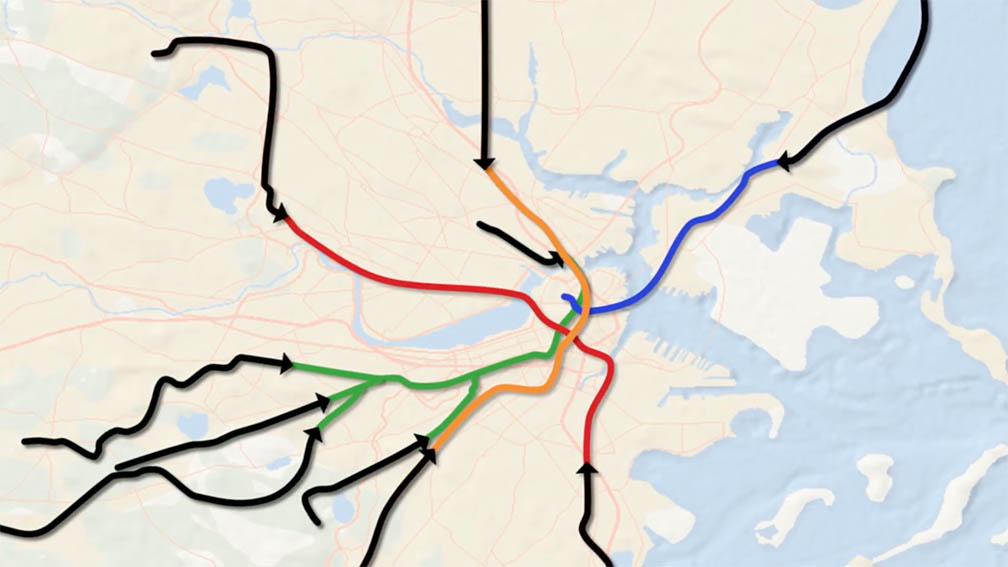
Markian Borkowsky MCRP’20 spent several years studying and working in Boston, where he was dependent upon buses, trolleys, and subways to get to classes, socialize with friends, and explore the region. Often frustrated with the “radial” or downtown-focused design of the system, where riders have to travel long distances downtown just to transfer to other lines even if their destination is not even near the downtown business center, he knew there had to be a better way.
As he entered his final semester of the Bloustein School’s Master of City and Regional Planning program this past spring, the choice of an independent study elective provided an opportunity to have the full creative freedom to build his own solution to this problem. He went into his first class with a single idea—a new bus line for Boston.
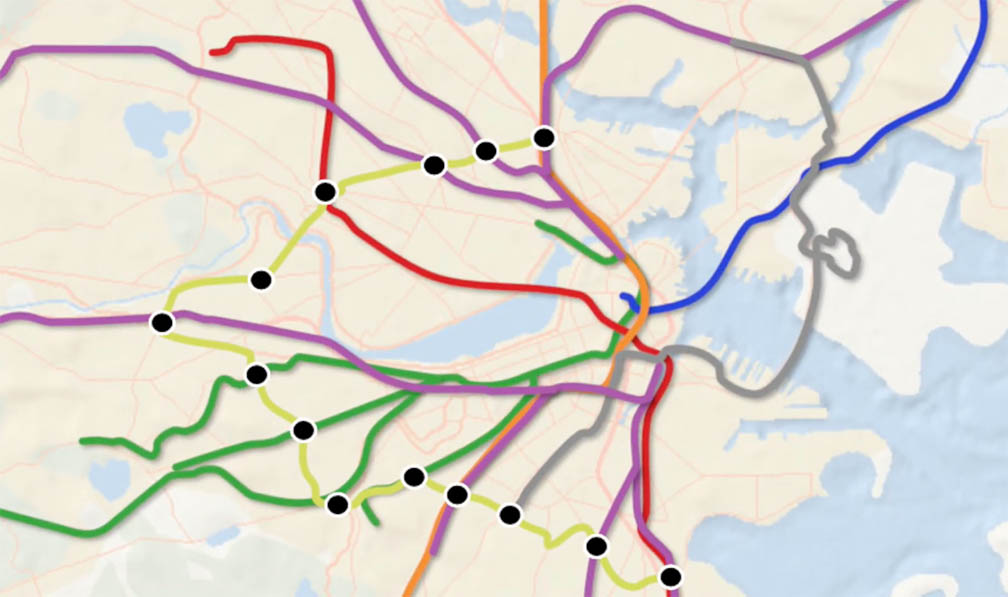
“I created a new regional connector bus line, the “R-Line,” for the Greater Boston Metropolitan Area,” said Markian, who spent 14 busy weeks developing and revising designs for a final eight-minute proposal video which he presented in May. “The video showcases the features of the R-Line and The Neuron Station, a mixed-use transportation and healthcare hub, and explains the importance of investing in reliable urban systems, like transportation and healthcare infrastructure.”
He explained that the alignment of the R-Line was largely based on the 66, his favorite Boston bus line, noting that this line already does a great job of connecting myriad rail lines in the city. However, street traffic frequently slows down the buses, and high ridership rates mean that vehicles can be overcrowded. “Using the 66 as my base, I extended its termini in Harvard and Dudley square to connect with even more rail stations. Being able to look at important data like housing density, job centers, hospitals, and universities helped me hammer down the route’s alignment with a more precise eye, as my overall goal was to create a line that moved as many people to as many important places in the city quickly and efficiently.”
After completing the line, he selected one station on the route to design as his hub. Knowing that the new line would connect many different centers in the Greater Boston Area he chose a station near the city’s healthcare district, Longwood Medical Center. His first job out of college was as a practice assistant in a surgical clinic in the area, so he already had a concrete mental picture of the current site and what needed improving. He was aware that the region’s horrible traffic, coupled with unreliable public transportation, greatly impacted patients’ availability to come in and made clinic flows for providers and admins difficult to manage. It also affected his coworkers’ ability to get to work on time. “At one point, I had to travel between two hospitals daily to work at different clinics for my job,” he said. “It was during these back and forth shuttle rides that I really started connecting the dots between these issues. It also helped greatly that I am a huge transit enthusiast and spent many hours looking at and researching public transit lines and systems, as well as spent many hours riding transit abroad when I studied in Madrid, Spain, for a semester.”
He knew from previous transportation planning classes that infrastructure improvements could speed buses up, but only if buses were given dedicated lanes fully separated from vehicle traffic. As a result, he planned the R-Line to be bus rapid transit (BRT) in nature, meaning buses run more frequently and stations have nicer amenities for passengers.
If he could provide more reliable transit for patients, he thought, maybe the entire health system would be strengthened as well, and people’s health could improve.
The Neuron Station presented in the proposal video began as a simple street-level bus stop with some improved crosswalks; after the initial design, professor Tony Nelessen challenged him to push the limits of the design. Having taken the bus many times to go to the hospital as a patient and discouraged by how far the bus stops were from main doors and lack of any weather protection or sidewalk improvements, the physical integration between the R-line and medical offices that interested him the most.
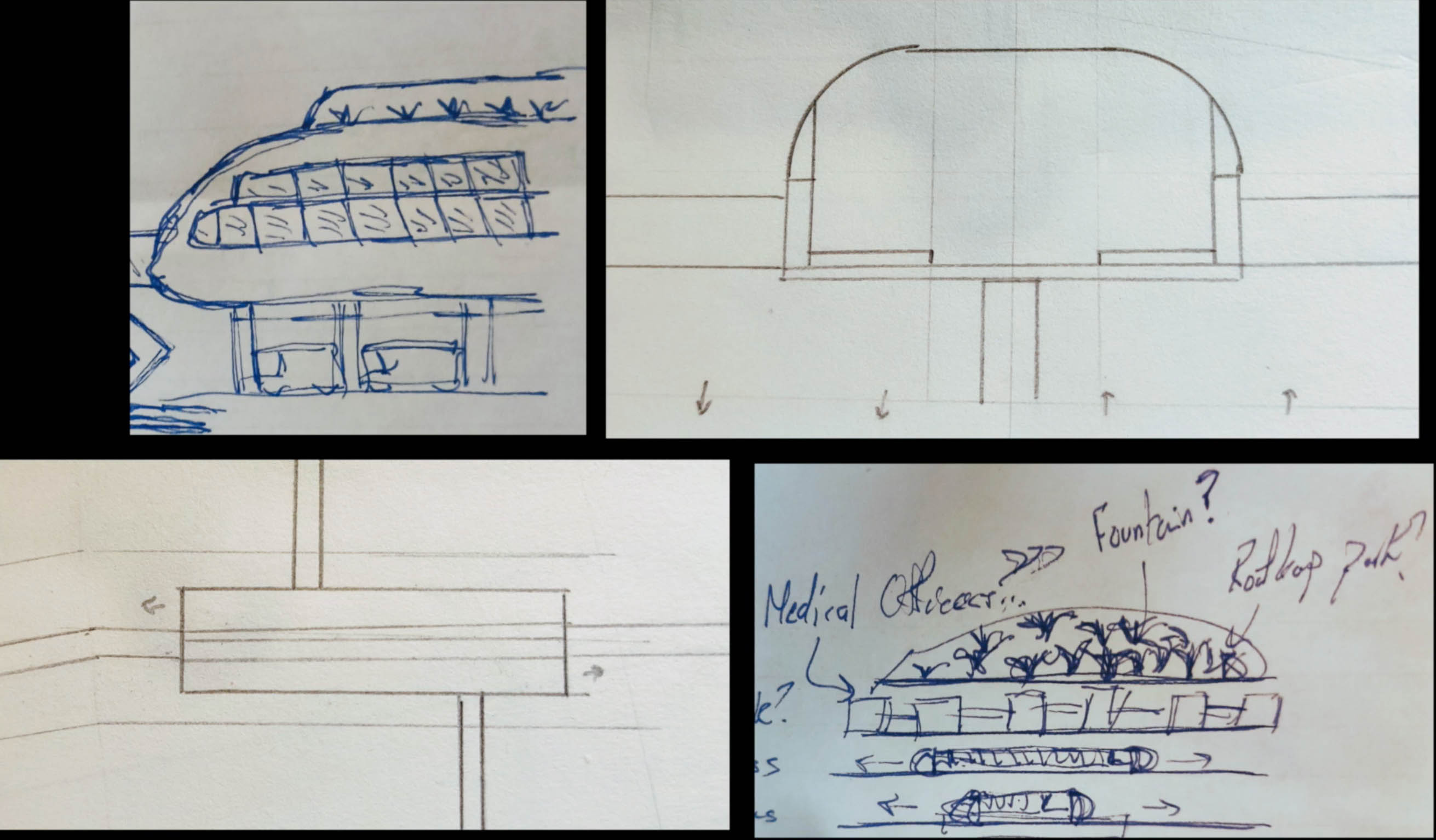
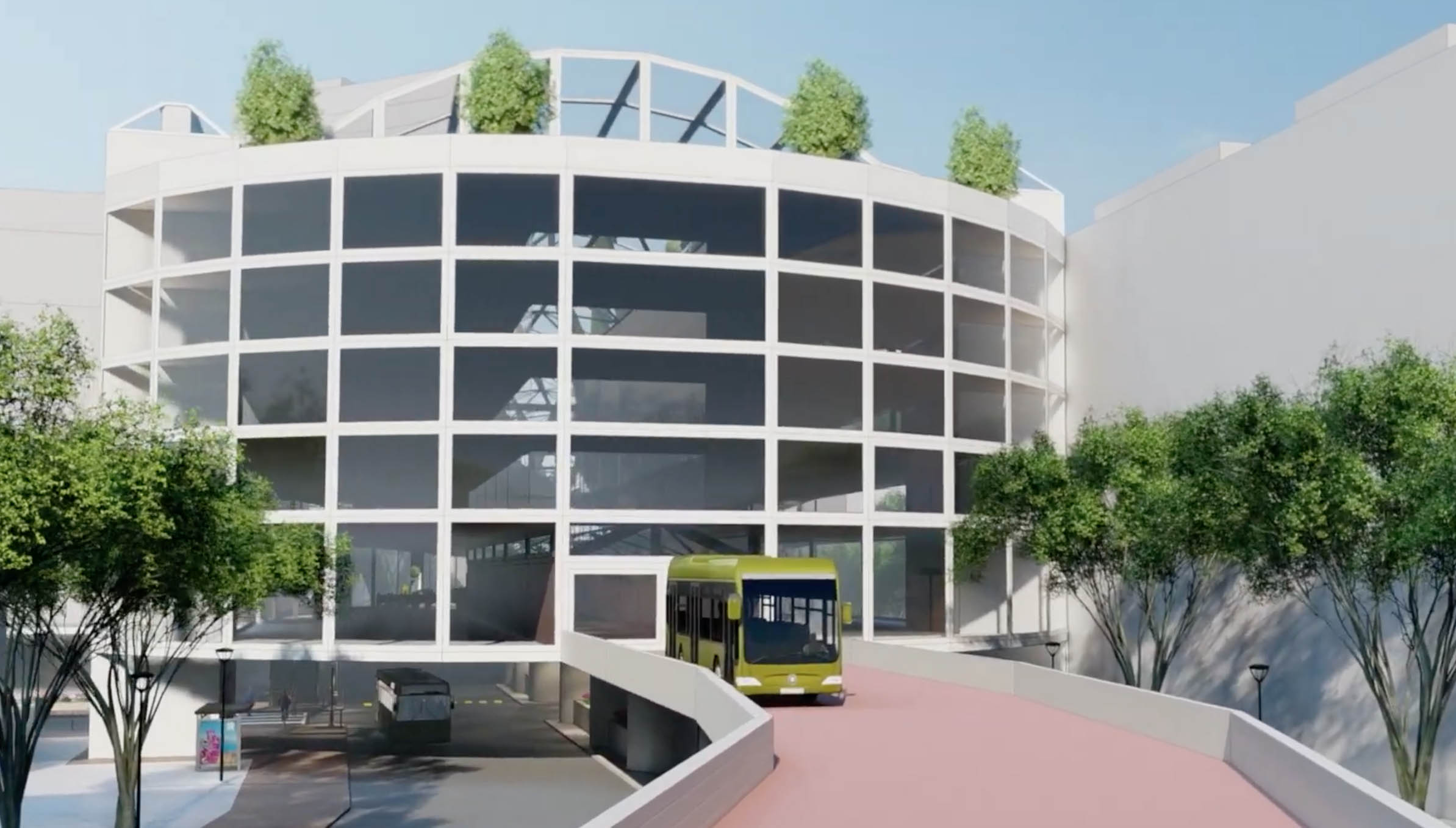
“This was when I realized that this project could be more than a bus line and station,” said Markian. “It was a call to provide sick urban residents, who rely on public transit to get to and from medical appointments, with a more integrated, reliable, and comfortable transit experience. After more thought, I realized that other groups would benefit from this type of transit integration as well, as healthcare workers could use the system to commute and hospitals could see increased patient flow.” He elevated the station and added healthcare offices above the station with bridges connecting to surrounding medical buildings.
It was important that the doctor’s offices and clinic spaces have access to natural light and green foliage, so he drew some of the station’s design from Kenmore Square, an existing bus station in Boston. The arching glass of the Kenmore Square allows for passengers to view the sky from under the station and provides warming sunlight during the cold Boston winters. “It was also a bit of nostalgia, as it was where I got on my first-ever city bus as a college freshman.”

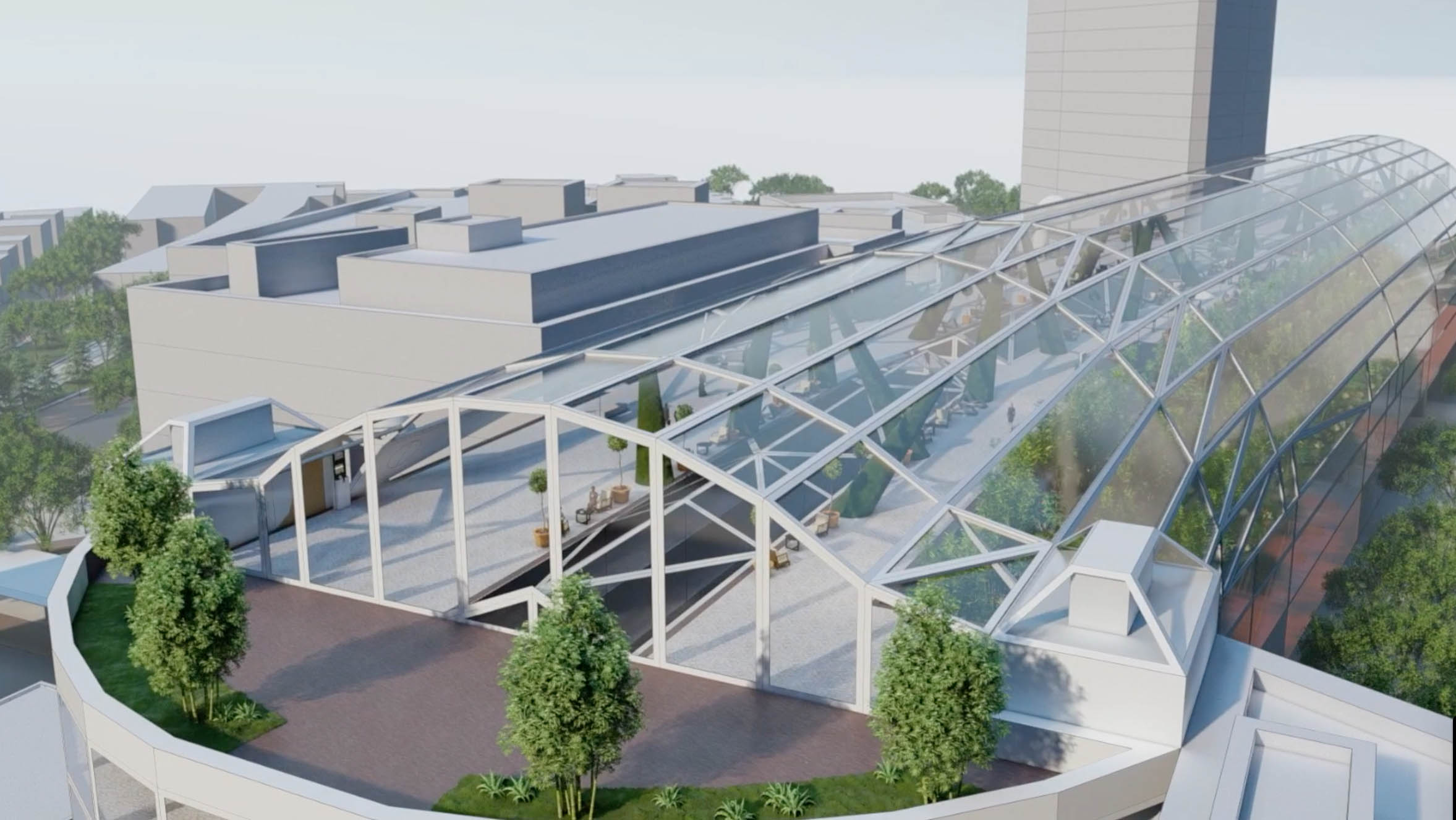
He embedded four main skylights through the spine of the station and built a tapered garden on four floors. “My favorite part of the station,” he noted, “Is the green roof park. It has large, ivy-covered columns holding the glass dome up for support. The columns intentionally resemble trees that spur out in different directions and keep the design of the space interesting for users.” As a former patient and healthcare worker, he is acutely aware that hospitals can be very stressful environments. He designed the rooftop garden to be a tranquil and reflective space, both figuratively and literally, so both workers and patients would have a place to unwind and ponder.
Reflecting on the completed project, one of the important lessons he learned is that there is no substitute for effective time management. “In 14 weeks, I created a proposal, designed the R-Line, built a 3-D model of the station, created high definition renders, and producing the proposal video,” he said. “This entailed working on the project every day and required a high level of self-motivation.
Having been provide a large project goal—the proposal had to have a video section—right at the start of the studio, was a key component of his success. “Professor Nelessen asked for this enormous final project, which mirrored what I would have to produce at a professional job,” Markian. “And while he did provide weekly goals to meet, I was able to work at my own pace. Rather than instruct, he acted as a mentor. He didn’t control the flow of my work but rather helped me stay on track and manage my time to keep me on schedule.”
Markian also discovered the value of the internet for learning new skills. Before this project, he had never utilized 3-D renderings or video editing software such as Lumion, Final Cut Pro, or Motion. Having resource guides and videos available on the internet was the only way—especially during the final 7 weeks under quarantine—that enabled him to finish this project on time.
“Most importantly, I learned that finding the creativity to create a project on this scale forced me to fundamentally challenge my overactive mind and commit to my ideas,” he said, “With such a short time frame, there was no space for second-guessing. I learned to embrace my ideas, even if I wasn’t 100% sure of them.”
Markian believes that this project was, by far, the most impactful experience of his graduate school career. By drawing from what he learned from in courses such as Public Transportation Management and Planning, Topics in GIS, History and Theory of Planning, and Survey of Planning Law Principles, he was able to produce a more comprehensive and salient final product.
A New Jersey native, Markian is happy with his choice to return and attend the Rutgers Master of City and Regional Planning Program. “The work I did on this project is comparable to a master’s thesis, and I am very happy with the final product,” he said. “I am incredibly grateful to the Bloustein School professors for the support they provided in answering my many questions during this process, and I loved working on planning and design projects where I could visit the physical site and gain first-hand insight into how the project should unfold. Currently, I am looking for planning positions in a wide range of fields and would love to continue working on how transit, healthcare, and design can function more effectively together to make our cities healthier places live, work, and play. I am excited to see what the future has in store.”
